Deciphering the Value of Additional Dimension in Google Analytics: Everything About Its Significance and Impact
In the world of electronic analytics, the utilization of additional measurements within Google Analytics offers as a critical device for critical much deeper layers of information understandings. The significance of additional measurements hinges on their capability to supply a nuanced view of customer behavior and communication with a website or platform. By exploring information beyond surface-level metrics, services can unlock a wealth of information that forms critical choices and refines advertising and marketing efforts. This exploration into the realm of second measurements not only uses an extensive understanding of user engagement but also clarifies the elaborate dynamics that drive on-line performance.
Understanding Additional Measurements in Google Analytics
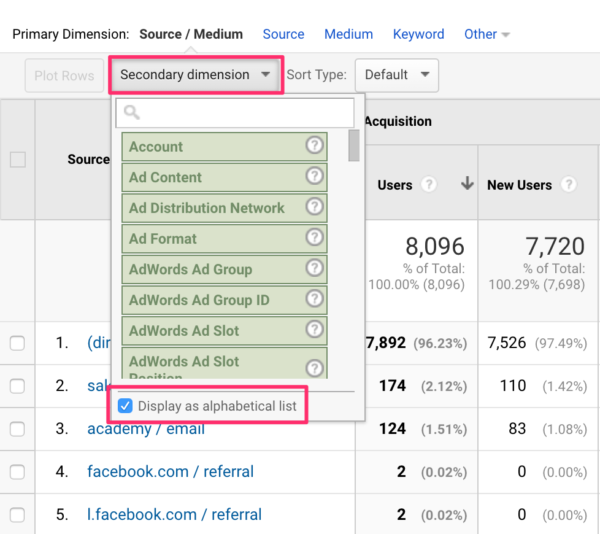
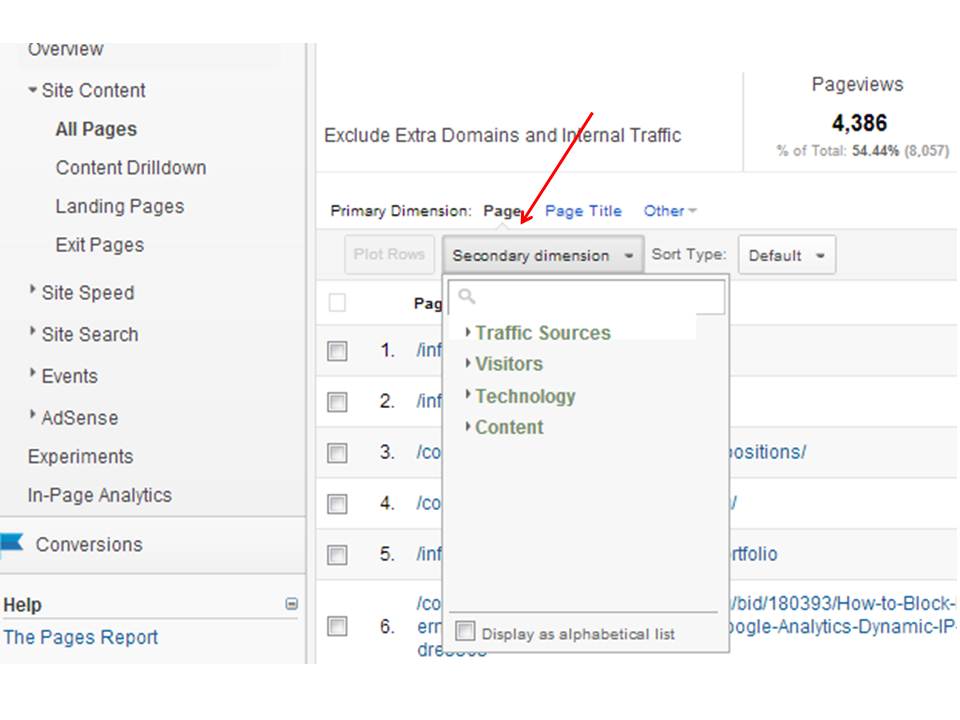
The understanding of additional dimensions in Google Analytics is important for obtaining deeper insights right into individual habits and website efficiency. While main measurements provide essential data factors such as traffic sources and web page sights, secondary measurements enable a more nuanced evaluation by giving additional context to these key metrics. By including secondary dimensions, users can sector and filter their data to uncover patterns and trends that may not be quickly apparent.

Unveiling the Advantages of Secondary Measurements
Building upon the foundational understanding of secondary dimensions in Google Analytics, discovering the advantages they offer discloses very useful understandings for enhancing information evaluation and decision-making. By incorporating second measurements, customers can dive deeper into their data, obtaining a much more extensive view of user actions, content efficiency, and other essential metrics. Among the key advantages is the ability to segment information, enabling an extra granular analysis of numerous measurements such as web traffic sources, devices, demographics, and a lot more. When looking at data in accumulation., this division makes it possible for individuals to identify patterns, fads, and relationships that may not be obvious (what is a “secondary dimension” in google analytics?).
Moreover, additional measurements provide context to key information, providing extra layers of info that can help in comprehending individual interactions and preferences. This enhanced understanding can direct calculated decision-making, causing even more targeted advertising and marketing projects, website optimizations, and total better performance. Basically, additional measurements offer as a powerful tool for opening deeper insights and taking full advantage of the energy of Google Analytics for services and internet site owners.
Leveraging Second Measurements for Enhanced Insights
By using the power of second measurements in Google Analytics, companies can reveal deeper insights that drive educated decision-making and strategic optimization efforts. Leveraging additional measurements allows organizations to delve past surface-level information and get a much more extensive understanding of individual habits, audience check this site out demographics, traffic sources, and internet site performance. By incorporating key measurements like website traffic resources with second measurements such as geographical location or device classification, companies can determine which regions or gadgets are driving the most useful web traffic to their website.
Additionally, secondary dimensions make it possible for companies to section and examine information better, aiding them recognize patterns, patterns, and chances that may have otherwise gone undetected. By utilizing second measurements, businesses can tailor their advertising strategies, content, and user experience to better satisfy the needs and preferences of their target audience. Essentially, leveraging secondary measurements in Google Analytics empowers companies to make data-driven choices that lead to boosted performance, boosted ROI, and sustainable growth.
Impact of Second Measurements on Data Analysis
Enhancing data evaluation through the utilization of additional dimensions in Google Analytics offers organizations with a much deeper understanding of their online performance metrics. By including secondary measurements, such as time of day, geographical location, or device classification, businesses can discover valuable understandings that might have been ignored with primary measurements alone. This improved level of granularity enables more exact segmentation of data, enabling services to identify patterns, fads, and relationships that can drive strategic decision-making.
Making The Most Of Prospective: Second Dimensions Approaches
One crucial strategy is to integrate second measurements with primary dimensions to acquire a comprehensive sight of individual interactions. Combining the primary measurement of 'source/medium' with additional dimensions like 'touchdown web page' or 'tool group' can expose which networks are driving website traffic to details web pages or exactly how individual actions varies across devices.
Moreover, making use of second dimensions to sector data based on customer demographics, actions, or innovation can aid services tailor their advertising and marketing initiatives to details audience sectors. This targeted method can lead to improved conversion rates, improved user experiences, and inevitably, boosted ROI. By taking full advantage of the potential of second dimensions in Google Analytics, organizations can make educated choices, enhance their online visibility, and drive lasting growth.
Final Thought
To conclude, secondary dimensions in Google Analytics play an important duty in giving deeper understandings and enhancing information evaluation. By utilizing second dimensions effectively, organizations can get a much more extensive understanding of individual actions and internet site efficiency. Incorporating additional dimensions right into data evaluation approaches can bring about even more informed decision-making and boosted total performance. It is essential for organizations to utilize the power of additional measurements to optimize their possible and attain better success in their online endeavors (what is a “secondary dimension” in google analytics?).
While primary measurements give basic data factors such as traffic resources and page sights, second measurements enable for a much more nuanced analysis by providing added context to these main metrics. By combining key dimensions like website traffic sources with second measurements such as geographic place or tool classification, companies can identify which areas or tools are driving the most important web traffic to their find website.
By integrating secondary dimensions, such as time of day, geographic location, or gadget category, organizations can reveal important insights that might have been ignored with key dimensions alone. One key technique is to integrate secondary measurements with main measurements to acquire an extensive sight of user communications. Combining the primary measurement of 'source/medium' with secondary dimensions like 'touchdown web page' or 'tool group' can reveal which networks are driving traffic to certain web pages or just how user behavior varies throughout tools.